Why Must A Disaster Plan Be Continually Revisited And Updated?
Business continuity (BC) and disaster recovery (DR) are closely related practices that back up an organization'southward ability to remain operational after an agin event.
Resiliency has go the watchword for organizations facing an assortment of threats, from natural disasters to the latest round of cyberattacks.
In this climate, business organisation continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) has a higher profile than e'er before. Every arrangement, from small-scale operations to the largest enterprises, is increasingly dependent on digital technologies to generate revenue, provide services and support customers who always await applications and data to be available.
"Mission-disquisitional information has no time for downwards time," said Christophe Bertrand, a senior analyst who covers information protection for Enterprise Strategy Group (ESG), a market research firm in Milford, Mass. "Even for non-critical information, people have very lilliputian tolerance."
Disruption isn't just an inconvenience for customers. A fire, flood, ransomware set on or other malady can rack up financial losses, damage the corporate make and, in the worst-case scenario, shutter a business concern permanently. About a third of the respondents to Uptime Institute's 2019 Global Data Center Survey reported having "business impacts" linked to some form of infrastructure in the past year. A chip more than 10% of the respondents said their nigh contempo outage resulted in $1 million-plus in directly and indirect costs.
"These outages increasingly span multiple information centers, and best practices dictate comprehensive and ongoing resiliency reviews of all company-owned and third-party digital infrastructure," according to Uptime Constitute, a Seattle-based data eye standards organization.
Why is BCDR important?
The role of BCDR is to minimize the effects of outages and disruptions on business concern operations. BCDR practices enable an organization to get dorsum on its feet after problems occur, reduce the risk of data loss and reputational impairment, and ameliorate operations while decreasing the chance of emergencies.
Some businesses might have a head offset on BCDR. DR is an established role in many It departments with respect to individual systems. However, BCDR is broader than IT, encompassing a range of considerations -- including crisis management, employee rubber and alternative work locations.
A holistic BCDR approach requires thorough planning and training. BCDR professionals can help an organization create a strategy for achieving resiliency. Developing such a strategy is a circuitous process that involves conducting a business impact analysis (BIA) and risk analysis every bit well every bit developing BCDR plans, tests, exercises and grooming.
Planning documents, the cornerstone of an effective BCDR strategy, also help with resource management, providing information such every bit employee contact lists, emergency contact lists, vendor lists, instructions for performing tests, equipment lists, and technical diagrams of systems and networks.
BCDR practiced and consultant Paul Kirvan noted several other reasons for the importance of BCDR planning:
- Results of the BIA identify opportunities for procedure comeback and ways the arrangement tin can use technology better.
- Information in the plan serves as an alternate source of documentation.
- The programme provides a single source of key contact information.
- The plan serves as a reference document for use in product planning and design, service design and delivery, and other activities.
An arrangement should strive for continual improvement, driven past the BCDR process.
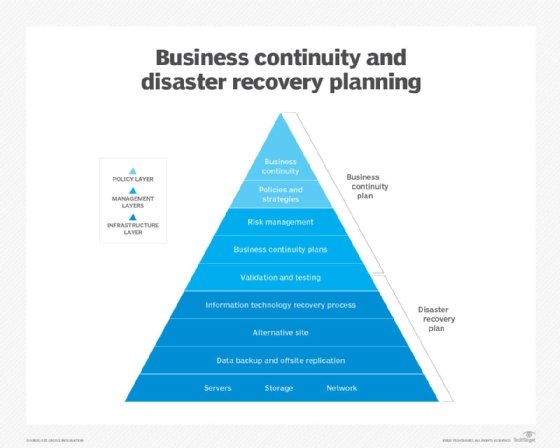
What is business concern continuity and disaster recovery?
BC and DR are closely related practices that back up an system's power to remain operational after an adverse event. The goal of BCDR is to limit risk and become an organization running as shut to normal as possible after an unexpected interruption. These practices enable an organization to go dorsum on its feet after problems occur, reduce the risk of data loss and reputational damage, and improve operations while decreasing the chance of emergencies.
The trend of combining business organization continuity and disaster recovery into a single term, BCDR, is the outcome of a growing recognition that concern and technology executives demand to interact closely when planning for incident responses instead of developing schemes in isolation.
What's the difference between business continuity and disaster recovery?
BC is more proactive and by and large refers to the processes and procedures an organisation must implement to ensure that mission-critical functions can continue during and after a disaster. This area involves more than comprehensive planning geared toward long-term challenges to an organization's success.
DR is more than reactive and comprises specific steps an organization must accept to resume operations following an incident. Disaster recovery actions take place after the incident, and response times can range from seconds to days.
BC typically focuses on the organisation, whereas DR zeroes in on the technology infrastructure. Disaster recovery is a slice of business continuity planning and concentrates on accessing information easily post-obit a disaster. BC includes this element, only also considers take a chance management and other planning an organisation needs to stay adrift during an upshot.
In that location are similarities betwixt business organisation continuity and disaster recovery. They both consider various unplanned events, from cyberattacks to human error to a natural disaster. They also take the goal of getting the concern running as close to normal as possible, particularly concerning mission-critical applications. In many cases, the same team is involved with both BC and DR.
What'southward the difference between business organization resilience and business continuity?
Business resilience andresiliency began appearing in the BCDR vocabulary in the early 2000s. Resilience, at times, has been used interchangeably with business organisation continuity, simply the terms have different shades of pregnant.
Kirvan said a resilient business can return to its previous operational state following an event that shut it down. Business continuity management, technology disaster recovery and incident response are among the disciplines that fuel an organisation'southward resiliency.
Resilience focuses on building a business to be impervious to potential disruptions of various kinds, according to Jeff Ton, senior vice president of product development and strategic alliances at InterVision Systems, an IT service provider with regional headquarters in Santa Clara, Calif., and Chesterfield, Mo. Concern continuity, in contrast, involves resuming operations from an outage once it has occurred, Ton noted.
Resiliency "is more almost being able to resist and withstand issues, and business organization continuity is about being able to continue business later something has disrupted your business," Ton said.
Using a condom band analogy, Ton said an event might stretch an arrangement, but, if resiliency has been achieved, it resists and reassumes its shape. Business organization continuity kicks in when the rubber band snaps and the organization takes steps to address the breakage, he added.
Bertrand said business continuity revolves around the power to fail over and maintain systems at a loftier level of availability, while resilience is the ability to resist disruption and prevent bug from happening in the first identify.
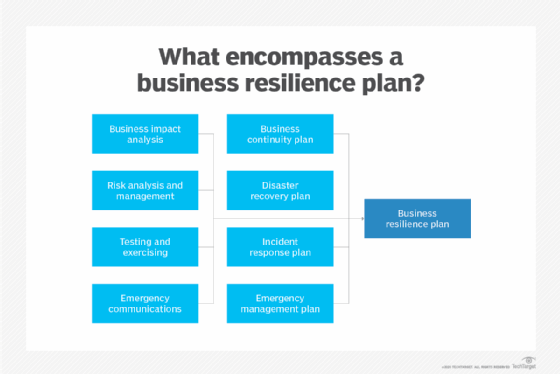
The role of chance analysis, business impact analysis and BCDR strategies
Adventure analysis and BIA are critical tools for organizations facing the question of how to build a BCDR strategy.
Determining internal and external risks is important to the BCDR process. The risk analysis identifies risks and the likelihood they will occur. This take chances assessment works in tandem with the BIA, which helps quantify the potential effects of disruption. Financial analysis is one aspect of a BIA, but this exercise also considers the non-fiscal costs of unplanned outages. In add-on, the BIA identifies the mission-critical functions an organisation must maintain or restore post-obit an incident, and the resources needed to support those functions.
It'due south important to gain management support when pursuing a BIA, given the intensity of the process. The BIA provides a way for an organization to learn virtually itself and details opportunities for improvement.
An organization uses adventure analysis and BIA information to determine business organization continuity and disaster recovery strategies and the appropriate responses. Each strategy is turned into a series of actions that will help accomplish operational recovery, such as data replication, failing over to a deject-based service, activating alternate network routes and working remotely.
Why should you lot utilize BCDR, and when should information technology be activated?
Motivations for an arrangement developing a BCDR strategy might include protecting the lives and safety of employees, ensuring the availability of services to customers and protecting revenue streams. Competitive positioning and reputational management are factors that often underlie other motivators: A business perceived every bit unable to protect employees or evangelize services volition struggle to attract workers and customers.
The regulatory and compliance environment also influences organizations in their pursuit of BCDR. The Health Insurance Portability and Accessibility Act Security Rule, for example, requires covered entities such as hospitals to provide an emergency mode operation program, which includes "procedures to enable continuation of critical business procedure for protection of the security of electronic protected wellness information."
The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), an organisation that oversees banker-dealers, requires firms to "create and maintain written business continuity plans" that address emergencies or disruptions to the business. FINRA spells out its required business continuity measures in its emergency preparedness dominion.
U.S. federal agencies, meanwhile, are also required to develop BCDR strategies, which in government terminology are chosen continuity of operations plans. The aim is to "ensure that essential government services are available in emergencies -- such as terrorist attacks, severe weather, or building-level emergencies," according to the Regime Accountability Office.
Customers might also put pressure on organizations to develop acceptable BCDR plans. An assessment of a concern' BCDR stance might be part of a prospective customer's vetting process. Federal regulators, such as the Part of the Comptroller of the Currency, encourage banks to include resilience equally part of the vendor due diligence procedure. Specifically, OCC Message 2013-29, Third-Party Relationships: Risk Management Guidance, states that banks should "determine whether the third party maintains disaster recovery and business continuity plans that specify the time frame to resume activities and recover information."
The "why" of BCDR potentially has many answers, and the "when" of business continuity and disaster recovery is similarly nuanced. Organizations must weigh several factors before declaring a disaster and triggering the BCDR programme. Principal among those are the expected elapsing of the outage, the outage's effects on the organization, the financial cost of activating the BCDR plan and the BCDR plan'southward potential for causing disruption. Paradoxically, the process of failing over from an organization's primary identify of business to a backup facility -- and and then failing back after an event -- might significantly interrupt operations, noted Paul Thomann, regional principal, cloud and data centre transformation at Insight Enterprises Inc., an Information technology services provider based in Tempe, Ariz.
Appropriately, an organization'due south leadership must advisedly size up when to enact the BCDR plan. Migrating to a backup facility, Thomann said, "comes with an touch on to the budget." An organization, for case, might deem a half-dozen-hour outage not meaning plenty to make the disaster call.
That decision, particularly in larger enterprises, is typically made by a committee, rather than an private executive, Thomann said. The committee might consist of the CEO, CFO, CIO and other C-suite executives, he added.
How to build a BCDR plan
Organizations tin pause down a BCDR program into BC and DR components.
Specifically, according to BCDR consultant Kirvan, a business organization continuity program (BCP) contains contact information; change direction procedures; guidelines on how and when to utilize the plan; step-past-stride procedures; and a schedule for reviewing, testing and updating. A disaster recovery plan (DRP) features a summary of key action steps and contact information, the defined responsibilities of the DR squad, guidelines for when to use the programme, the DR policy argument, plan goals, incident response and recovery steps, hallmark tools, geographical risks and plan history. The DRP should also take staffing into business relationship, ensuring that personnel able to execute the various steps of a DR plan are ever available to enact critical recovery tasks.
Good business continuity and disaster recovery plans are articulate about the varying levels of risks to the organization; provide well-defined and actionable steps for resilience and recovery; protect the system'southward employees, facilities and make; include a communications plan; and are comprehensive in detailing deportment from beginning to end.
A BCDR policy is an of import initial step. The policy sets the foundation for the process and typically covers the scope of the business continuity management system, which employees are responsible for information technology, and the activities performed, such every bit plan development and BIA. A policy might besides plant a common set of metrics, such as key functioning indicators and key gamble indicators. The policy attribute is often disregarded, just information technology'southward an important business continuity auditing item.
Developing the BCP and DRP typically starts past gathering BCDR team members and performing a run a risk analysis and BIA. The system identifies the most critical aspects of the business, and how rapidly and to what extent they must be running afterward an incident. Afterwards the organization writes the footstep-by-footstep procedures, the documents should be consistently tested, reviewed and updated.
Although certain aspects of the process involve select members of the organization, it'south of import that anybody understand the program and is included at some betoken. The plan should likewise comprehend 3rd parties and the services they provide. A bank, for example, might rely on data that a third-party firm supplies, so the relationship should be documented in the BCDR plan. Such outside entities must be kept in the loop so that they understand how the plan is going to work.
Other steps in a BCDR planning checklist include risk mitigation and an emergency communications plan. The latter details the method, or methods, an arrangement will use to disseminate information on an emergency to employees.
In summary, the process of building a BCDR plan will typically involve the following activities:
- take chances identification
- infrastructure review
- business bear on assay
- program blueprint
- plan implementation
- testing
BCDR testing
Testing a business concern continuity and disaster recovery program provides assurance that the recovery procedures put in place volition work every bit expected to preserve business operations. The testing phase might also highlight areas for improvement, which the organisation tin address and contain into the next version of the plan.
Tests can range from simple to complex. A discussion-based tabletop exercise brings together participants to walk through the program steps. This type of test helps employees with BCDR roles go more than familiar with the response process, while letting administrators assess the effectiveness of the BCDR plan.
On the other end of the testing spectrum, a full-scale test simulation calls for participants to perform their BCDR functions rather than discussing them in a tabletop practice. These drills might involve the utilize of backup systems and recovery sites.
Testing, however, requires time, funding, management support and employee participation. The testing process besides includes pretest planning, training exam participants and reporting on the test.
The frequency of testing varies by organization. Larger enterprises should comport tabletop exercises at least quarterly, while smaller organizations can test less frequently, Insight Enterprises' Thomann said. A full BCDR exam, which is more time- and resources-intensive, tin can exist conducted annually, he added.
InterVision's Ton also recommended a quarterly testing schedule, with a DR test conducted twice a yr with tabletop exercises in between those tests. Business continuity, equally a separate test, tin be conducted annually. Ton said he'southward found it more effective to carve up the tests considering conducting the DR on its own examination is less disruptive to the organization.
Periodic testing, plan maintenance and resilience are interrelated. An organization improves its resilience when information technology updates its BC and DR plans and and then tests them continually.
BCDR cost direction
Changes in the threat landscape or new business ventures might compel an organization to expand its BCDR coverage. That change in scope could call for spending on consulting services or backup and disaster recovery technologies.
BCDR managers might need to seek new funding for the expanded BCDR plan and resilience technologies if the dollars aren't available in the electric current upkeep.
An investment proposal should be built on a business case that emphasizes the positive results the new BCDR capabilities will provide for the organization. The bid for funding should also determine whether the revised BCDR plan will affect other areas, such as cybersecurity. Other steps toward obtaining funding include vetting products and services that support the expanded requirements and preparing a procurement asking with enough documentation, according to BCDR consultant Kirvan.
Ton said organizations should strike a balance between the level of investment in BCDR approaches and the anticipated financial effects of a given disaster scenario. "You don't want to come up with a solution that costs 200 times more than than the disaster would take," he said.
Asking business concern leaders from various corporate disciplines to estimate the expected costs associated with unlike types of events can help organizations establish a baseline from which they tin make informed BCDR investment decisions.
Standards, templates, software and services for BCDR planning
Organizations embarking on a business continuity and disaster recovery planning process have numerous resources to draw upon. Those include standards, tools ranging from templates to software products, and advisory services.
"To build a plan, you lot have many templates that exist and many all-time practices and many consultants," ESG's Bertrand said. "There's no reason not to have a strong DR plan."
BCDR standards
Regime and private sector standards bodies, including the National Found of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), accept published BCDR guidelines. The standards, which cover topics from crisis direction to hazard assessment, provide frameworks on which businesses can build their BCDR plans.
The following is a sampling of standards:
- ISO 22301:2019: Security and resilience -- Business organisation continuity direction systems -- Requirements
- ISO 22313:2012: Societal security -- Concern continuity management systems -- Guidance
- ISO 22320:2018: Security and resilience -- Emergency management -- Guidelines for incident management
- ISO/IEC 27031:2011: Information technology -- Security techniques -- Guidelines for information and communication technology readiness for business continuity (being redeveloped as ISO/IEC WD 27031)
- ISO 31000:2018, Risk direction -- Guidelines
- ISO Guide 73:2009: Gamble management -- Vocabulary
- IEC 31010:2019: Chance management -- Risk cess techniques
- ISO/TS 22317:2015: Societal security -- Concern continuity management systems -- Guidelines for business affect analysis (BIA) (to be replaced past ISO/AWI TS 22317)
- FINRA Dominion 4370: Business Continuity Plans and Emergency Contact Data
- National Fire Protection Association 1600: Standard on Continuity, Emergency, and Crisis Direction (new consolidated draft pending)
- NIST Special Publication 800-34 Rev. ane: Contingency Planning Guide for Federal Data Systems
- American National Standards Institute/ASIS ORM.1.201 Security and Resilience in Organizations and Their Supply Chains
Business continuity and disaster recovery plan templates
Templates provide preset forms that organizations can fill out to create BCDR planning documents. Some templates cover the BCDR programme as a whole or address particular aspects of the BCDR planning.
This general BCP, for case, includes provisions for natural disasters, fires, network service provider outages and floods or other water damage. A planning template can also assist SMBs, which could simplify the process, depending on organization's size and complexity.
A BCDR plan might telephone call for a service-level agreement (SLA), which sets standards for the quality of an organization's BCDR recovery program. They tin besides aid ensure services obtained through 3rd parties, such every bit DR hot sites, perform at acceptable levels. This template addresses SLAs for BCDR programs.
As noted in a higher place, conducting a BIA can help organizations with business continuity planning. This BIA written report template provides a mechanism for documenting parent process, subprocesses and the fiscal and operational effects in the event of an interruption.
Organizations can too benefit from scheduling BCDR activities for the ongoing care and maintenance of business continuity strategy. Activities range from scheduling a BIA to reviewing a technology disaster recovery program.
BCDR software
Specialized BCDR software provides another tool for organizations ready to build a plan. BCDR products, sometimes referred to as business organisation continuity software or business continuity direction software, aim to assistance organizations build business continuity and disaster recovery plans. They typically embrace a range of planning activities, such as BIA and risk assessment, and offer incident response capabilities.
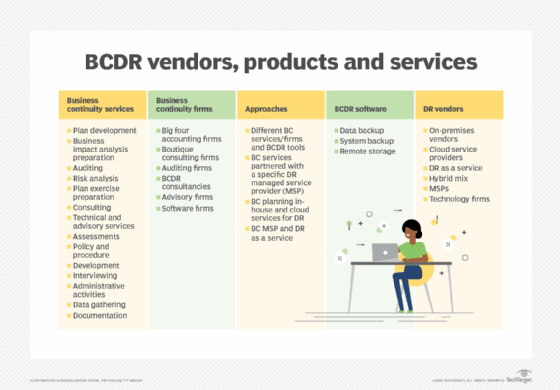
Vendors in the market include Balls Software, Avalution Consulting, Continuity Logic, Dell Technologies (RSA Security), eBRP Solutions, Fusion Risk Management and SAI Global.
BCDR planning services
Another selection is to outsource the organization'southward BCDR needs to a tertiary-party business firm that can provide risk analysis, plan development and maintenance, and training. It's incumbent upon the business to clarify its needs before selecting a BCDR business firm, nailing down such information as what it wants to outsource, what services information technology expects of the vendor, the risks of an outsourcing agreement and how much it plans to spend.
Potential sources of planning support include accounting firms, which can perform BIAs as office of the business continuity planning process. Accounting firms should typically exist able to assist clients determine the cost of workload outages, merely buyers should ideally select a firm with experience in business organization continuity or IT resource planning, according to writer and former CIO Brien Posey. Consulting firms can likewise assist with BCDR planning, Posey added.
Managed service providers (MSPs) often serve as virtual CIOs for their SMB customers. In that office, MSPs tin help with planning. Considering their business is to manage a customer'southward Information technology assets, they are able to develop a programme for dealing with technology outages.
Supporting technologies and strategies
The technology options for executing the DR portion of a BCDR plan accept expanded in recent years due to the advent of deject computing. Traditionally, organizations built or hired out an off-site facility to handle their disaster recovery needs. Such disaster recovery sites require a duplication of in-firm product systems, so they could prove out of the financial reach of many SMBs. Even so, cloud-based offerings such every bit disaster recovery as a service have made DR more than accessible for smaller organizations.
Other resilience offerings include emergency notification systems, cybersecurity systems and incident response systems, which might be included in business continuity management products. Organizations might also tap work expanse recovery vendors that provide alternative work locations for employees.
BCDR management
The team that builds, manages and, in the consequence of a disaster, executes a BCDR plan should exist cross-functional, cartoon upon multiple stakeholders and pockets of expertise across the organization.
The team'south leadership varies somewhat by arrangement. In a large enterprise, for example, the gamble management officer often chairs the BCDR squad with a representative from the It department as a vice chair, Ton said. Smaller organizations lacking a chance management department might appoint the CFO to lead the team, he noted. And, in some cases, the IT section head might direct the BCDR squad.
Other members of the team typically include representatives from the arrangement's key business organization functions: finance and accounting, facilities, legal -- including in-business firm and exterior counsel -- marketing and public relations, for case.
The task of pulling multiple stakeholders together to develop a BCDR plan -- and conducting the necessary impact and adventure analyses -- can prove challenging. Projection direction thus becomes an important consideration. Organizations should recollect about appointing a project manager to shepherd the process of building a BCDR plan, Ton noted.
The BCDR team should likewise take on the task of ongoing concern continuity management, making sure plans are up to appointment. Business initiatives and data center technologies change often, so BCDR plans will need regular maintenance to stay on point. As a starting time stride, an organization should assess if the current plan tin be updated or whether an entirely new plan is in order, according to George Crump, president of Storage Switzerland, an Information technology analyst house. Organizations should conduct BCDR testing to determine the extent to which a program needs to be overhauled.
In addition to testing, a BCDR team might also want to consider a business continuity plan inspect, which assesses the effectiveness of a plan. The audit should item the risks that could threaten the program's success and test the controls currently in place to determine whether those risks are acceptable to the organization. An IT General Controls audit tin can too be used to appraise risks to the infrastructure and identify areas for comeback, according to BCDR consultant Kirvan.

The various roles and responsibilities of BCDR team members -- from planning to testing -- can be detailed in an organization's business continuity policy. Such a policy might besides encompass external personnel, such as vendors and customers.
Another aspect of BCDR teambuilding is getting individuals upward to speed on BCDR best practices. To that cease, BCDR team members can avail themselves of business organization continuity training and certification programs.
The Business Continuity Establish, a global professional organization, offers its Certificate of the Business Continuity Institute, which covers business continuity management process and do. The constitute besides offers a Business organization Continuity Management BCI Diploma for individuals looking for additional insight into concern continuity management.
The BCM Institute, meanwhile, offers its Business Continuity Certified Planner (BCCP) accreditation. The BCCP certification aims to recognize a business continuity professional person'south understanding of core business continuity management concepts.
Other organizations granting professional business concern continuity certifications include DRI International, the National Found for Business Continuity Direction and the International Consortium for Organizational Resilience. Such certification bodies usually work with an internal or external training group that prepare students to sit for exams, Kirvan noted.
Conferences likewise provide an opportunity to educate BCDR team members. Ton cited DRI and Disaster Recovery Journal events every bit helpful for people looking to learn more near business continuity.
BCDR pitfalls: Mind the gap
Change is perchance a BCDR plan's key nemesis. Every bit the footstep of engineering change accelerates, organizations are left updating Information technology equipment -- from storage and servers to networks and their associated devices. Some IT assets are moving to the cloud. A 5-yr-one-time BCDR plan is unlikely to reflect -- and prove acceptable to protect -- the current IT manor.
An organization's modify management procedure can help accost this issue. Alter direction oversees adjustments to systems, networks, infrastructure and documents. It addresses like situations as BCDR planning and testing, so an system might decide to include business organization continuity and disaster recovery in the change direction process.
The modify management process contains six major activities, according to Kirvan:
- identify a potential change;
- analyze the change request;
- evaluate the change;
- plan the modify;
- implement the change; and
- review and close out the alter process.
An arrangement, of form, is besides subject area to change. Organizations make acquisitions, divest non-cadre operations and create news lines of business, for example. An effective BCDR plan must be periodically updated to account for those developments. Regularly scheduled BCDR testing can expose gaps in the plan where information technology has failed to account for technology or business changes.
Perceptual gaps tin besides undercut BCDR plans. ESG'due south Bertrand said many organizations adopting software-as-a-service (SaaS) offerings have a imitation sense of security regarding data protection. A 3rd of the respondents to an ESG survey said SaaS apps such as Microsoft 365 and Salesforce don't need to be backed upwards. Bertrand said that's simply not the example. He cited the example of recovering email an organization's users have sent to the trash bin. He said Office 365, depending on the client's subscription level, retains deleted email for a limited time.
"SaaS application resilience is being conflated with SaaS data availability," Bertrand said. "SaaS-based applications are not beingness properly protected today."
Organizations using such cloud-based applications should become acquainted with their vendors' data protection and recovery SLAs and brand certain BCDR plans cover SaaS applications and their availability requirements. Bertrand said the percent of people who are aware of SaaS vendors' SLAs is improving, only not anybody is up to speed. He said 58% of ESG survey respondents said they were familiar with SaaS vendors' data protection and recovery provisions.
An system can employ a BCDR checklist, or a series of checklists, covering plans, policies and recovery strategies, to root out potential bug and flag BCDR weak points. The BCDR team should likewise stay abreast of the changing threat landscape to make sure their plans reverberate emerging threats. Business continuity risks that organizations should monitor range from evolving cybersecurity attacks to active shooter incidents.
The futurity of BCDR
BCDR planning and execution volition keep to evolve with the changing nature of threats. Here are a few developments to consider:
The confluence of cybersecurity and business continuity. The part of cyberattacks, such as ransomware, in disrupting business organization operations appears fix to continue, if not accelerate. Cybersecurity and concern continuity are typically separate and distinct functions in an arrangement. Kirvan, speaking on the future of concern continuity, said he believes those disciplines "ought to be under the same roof."
Going back to the future with tape storage. Backup files might exist encrypted in a ransomware attack. Organizations, all the same, can isolate the files they need for recovery from the corporate network, creating an air gap. That'southward where time-testing tape storage comes into play. Bertrand said tape storage is reemerging as a fashion organizations can preserve a "gilt copy" of their data, offline and off site. "Information technology'south coming back" he said of record.
AI'south influence on BCDR planning. AI and its cognitive functions might help BCDR teams make decisions on organizing their plans and might likewise play a function in conducting BIAs and risk assessments, according to Kirvan. AI could also support incident response, recommending actions based on the details of unfolding disaster scenarios.
Service providers play a bigger BCDR role. A large percentage of MSPs are involved in backup and disaster recovery. The MSP sector is likely to emerge as a i-stop store for business continuity services, particularly for SMBs lacking internal expertise. MSPs, in their trusted advisor role, tin advise clients on BCDR planning and make engineering science recommendations. Some provide their ain disaster recovery as a service, while others partner with vendors that provide that tool.
This was last updated in Feb 2020
Proceed Reading About What is BCDR? Business organization continuity and disaster recovery guide
- Larn more than about BCDR plans
- Apply this BCDR template to prepare for an agile shooter event
- Dig into the ISO 22330 business continuity standard
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchdisasterrecovery/definition/Business-Continuity-and-Disaster-Recovery-BCDR
Posted by: spenglerprinetheor.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Why Must A Disaster Plan Be Continually Revisited And Updated?"
Post a Comment